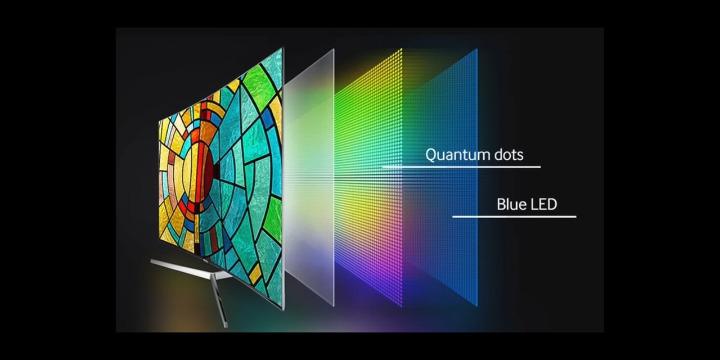
The biggest factor when finding the best product for you is understanding the different techniques that each TV has. In this case, it is OLED and LCD TVs. Below I will go over the basic of each different type and share with you their weaknesses side by side with their strengths. I’m also aiming to keep brief as if you are more interested in the actual work behind the scenes I’ve done an article on just that which you can find here.
It is a very knowledge-gaining topic most people think to buy the best technology TV but are confused about which one to buy. It will be more interesting when discussing the new technologies and comparing the visual display technologies. OLED (organic light-emitting diode) is the upgraded TV technology and the new one introduced and in the Tv/display market and it plays a very important role. The panel is supported by the hard pixel glass material which also protects the sensitive inner material.
What is LCD TV?
A very simple answer to what is an LCD TV is that it is a TV display technology depends on the liquid crystal display. LCD TVs consume less power when compared to plasma displays because they operate on the principle of blocking light instead of emitting it. An LCD display uses an active matrix screen grid or a passive matrix. The active matrix LCD is also known as a thin film transistor (TFT) display.
- Affordable
- Available in any size
- Bright and colorful
- Aging technology
- Narrow viewing angle
- Average contrast
What is OLED TV?
The best all-around TV that money can buy. That is the answer to what is an OLED TV. They offer the most high-end result while maintaining a relative cost to their performance, unlike QLED TV. In this case then, if you find yourself with a large budget and want a TV that will outperform all other TVs, then an OLED TV will be the best for you.
- The slimmest TV tech (2.57mm)
- Self-lighting pixels
- More convincing blacks
- Faster refresh rate (0.001ms)
- Judder and blur-free
- Only found in three screen sizes: 55, 65 & 77-inch
- Muted brightness (1,000nits)
- Expensive
| Features | LCD TV | OLED TV |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Minimum 1 inch | OLED TVs are smaller than LED TVs because of the volume of their diodes |
| Cost | Much cheaper | $9,000 – $15,000 |
| Power consumption | Requires less energy than plasma, but more than OLED TVs | Requires less power than LCD or Plasma TV |
| Screen size | 13 – 57 inches | Up to 55 inches (yet) |
| Burn-in | Not an issue | Burn-in is probable, but if the TV is damaged, OLED TVs may burn-in. |
| Backlight | Yes | No |
| Viewing angle | Up to 165°, Picture suffers from the side | 170-degree viewing angle |
| Used by | iPhone, HTC Sensation, iPad 2 | Samsung Galaxy S II, Samsung Galaxy Nexus, Nokia Lumina 800 |
| Motion Lag | Not a issue | To early to tell |
| Mechanism | Backlight enclosed by a liquid crystal layer | Organic Light-emitting diodes |
Comparing LCD and OLED:
OLED TV color information is generated using compounds based on organic carbon that emits red, green and blue light in response to electrical current. The main difference between OLED and LCD is that there is no backlight and no “twisting” crystals. And there is no extra light source required to energize the organic color compounds, so they use significantly less energy and can be produced with an incredibly thin profile. OLED TV panels arrive with two or three parts of organic compounds in one extremely thin “glass” coating.
LCD TVs replicate colors through a subtraction method: they separate specific color wavelengths from the white light spectrum until the correct pixel is entered. And it’s the light intensity allowed to move through this liquid-crystal matrix that allows LCD televisions to show chock-filled pictures of their colors or gradations.
Picture Quality
Color Reproduction: LCD TVs: LCD panels use a backlight that shines through a liquid crystal display to create colors. While modern LCD TVs have improved color accuracy, they may struggle to achieve the same level of color reproduction as OLED TVs. LCD panels may have slight variations in color accuracy and may not display the same depth and vibrancy as OLED panels.
OLED TVs: OLED TVs excel in color reproduction due to their unique self-emissive pixel technology. Each pixel in an OLED display produces its own light, allowing for precise control over individual pixels. This results in more accurate and vibrant colors, with better saturation and wider color gamut compared to LCD displays.
Contrast Ratio: LCD TVs: LCD displays use a backlight that illuminates the entire screen, which can lead to limited contrast ratios. While LCD TVs have improved over the years, they may struggle to achieve deep blacks and maintain optimal contrast in dark scenes. This can result in a loss of detail and less immersive viewing experience, particularly in low-light environments.
OLED TVs: OLED TVs offer superior contrast ratios as each pixel can independently emit light or turn off completely. When pixels are turned off, it creates true blacks, resulting in infinite contrast ratios. This ability to individually control pixels leads to exceptional detail in both dark and bright areas of the screen, enhancing the overall viewing experience.
Brightness Levels: LCD TVs: LCD panels can achieve higher brightness levels compared to OLED displays. They can produce brighter images, which can be advantageous in well-lit environments or rooms with high ambient light. LCD TVs with high peak brightness can offer better visibility and maintain image clarity in brightly lit conditions.
OLED TVs: While OLED TVs may not reach the same peak brightness levels as LCD displays, they compensate with exceptional black levels and contrast ratios. The ability to display deep blacks alongside bright colors provides a more dynamic and visually striking picture, especially in dark or dimly lit environments.
Viewing Experience
Viewing Angle: LCD TVs: LCD panels typically have more limited viewing angles, especially when compared to OLED displays. When viewing an LCD TV from off-center positions, colors may appear washed out, and the image quality may degrade. This limitation can impact the overall viewing experience, especially for larger screens or group viewing scenarios.
OLED TVs: OLED displays offer wide viewing angles with minimal color distortion, maintaining consistent picture quality even when viewed from extreme angles. This makes OLED TVs ideal for larger rooms or setups where multiple viewers can enjoy the same high-quality image from different positions.
Motion Handling: LCD TVs: LCD displays generally have fast response times, reducing motion blur and ghosting. However, some LCD TVs may exhibit motion lag or judder in fast-paced scenes or during rapid camera movements. This can result in less fluid motion representation, affecting the overall viewing experience, particularly for sports or action-packed content.
OLED TVs: OLED TVs have near-instantaneous response times, virtually eliminating motion blur and judder. They can display fast-moving objects with exceptional clarity, delivering smooth and fluid motion. This makes OLED TVs an excellent choice for watching sports, playing games, or enjoying action-packed movies.
Design and Thickness:
LCD TVs: LCD TVs are available in a wide range of designs, from slim bezels to more traditional frames. However, LCD panels still require a backlight source, which can limit the overall thickness and design possibilities. While LCD TVs can be aesthetically pleasing, they may not achieve the same sleek and minimalist appearance as OLED TVs.
FAQ
Are LCD or OLED TVs more suitable for well-lit rooms?
LCD TVs can provide higher peak brightness levels, making them more suitable for well-lit rooms or environments with high ambient light. The brighter images produced by LCD displays can help maintain visibility and image clarity in such conditions. However, OLED TVs compensate for their lower peak brightness with exceptional contrast ratios, allowing them to deliver a more visually striking picture, even in darker environments.
What is the lifespan of OLED TVs compared to LCD TVs?
The lifespan of both OLED and LCD TVs is generally long. However, OLED TVs may have a slightly shorter lifespan compared to LCD TVs. OLED panels can experience gradual luminance decay over time, known as “burn-out,” which can result in reduced brightness. Despite this, with normal usage, both OLED and LCD TVs can provide several years of reliable performance.
Can I use an OLED TV for gaming?
Yes, OLED TVs are well-suited for gaming. Their fast response times and motion-handling capabilities make them excellent choices for gaming enthusiasts. OLED displays can deliver smooth and fluid motion, reducing motion blur and providing an immersive gaming experience. However, it’s recommended to enable features like pixel shifting or screen savers to prevent potential burn-in from static gaming elements.
Are there any risks of image retention with LCD TVs?
LCD TVs are generally not prone to image retention or burn-in issues. Since they rely on liquid crystals to control light, there is no risk of permanent image retention. However, in rare cases, temporary image retention might occur but typically disappears quickly, and the display returns to normal functioning.
Final Words
When comparing OLED and LCD TVs, it’s clear that both technologies have their strengths and weaknesses. LCD TVs are more affordable, available in various sizes, and offer bright and colorful displays. However, they may struggle with color reproduction, have a narrower viewing angle, and limited contrast ratios.
On the other hand, OLED TVs provide exceptional picture quality with vibrant colors, deep blacks, and wide viewing angles. They also offer ultra-thin designs and superior motion handling. However, OLED TVs are currently available in limited screen sizes and can be more expensive